RayLoc-1: Shallow water experiment
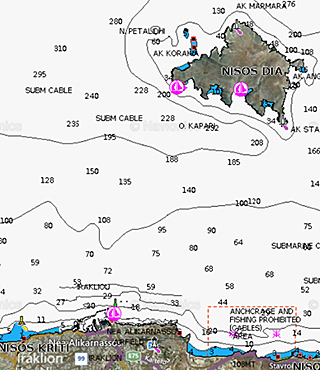
It is the first of the two basic experiments of SEAEARS program and involves detection of devices emitting pulsed sounds (pingers) in the water column or on the sea floor. The experiments were conducted in the Gulf of Heraklion between the port and the island of Día. The water depth in the experimental area was 140-180 meters. The following figure shows the region. In these experiments a broadband source (pinger) was used located either within the water column (at a depth of about 80 meters) or at the bottom (to a depth of 140-150 meters).
The main experiment Rayloc-1 was performed in 3 separate experiments named Rayloc-1A, Rayloc-1B, Rayloc-1C
Rayloc-1A
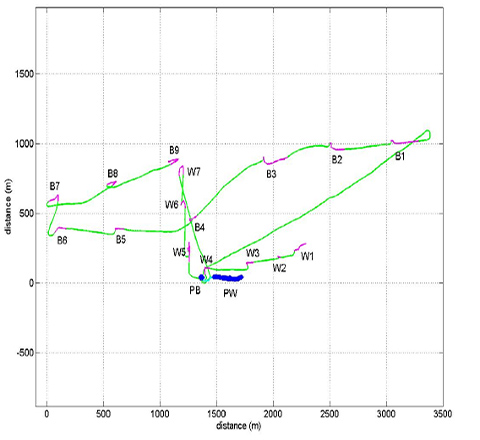
The RAYLOC_1A experiment was aimed at detecting an underwater acoustic source located either within the marine water column or at the surface of the seabed in shallow waters using two hydrophones and took place on 15 December 2014. The boat followed the path shown in the figure below where the boat course is the green line,(PB PW) is the pinger's position and the stations held in the experiment are shown in purple
Rayloc-1B
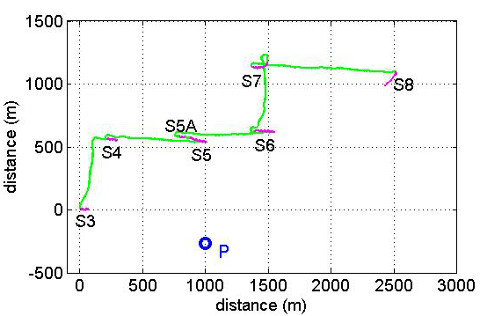
The RAYLOC_1Β experiment took place on April 24, 2015 and was aimed at detecting underwater acoustic source in real time. At this experiment were also used two hydrophones for the localization.The boat followed the path shown in the figure below where the boat course is the green line, (P) is the position of the pinger and the stations held in the experiment shown in purple
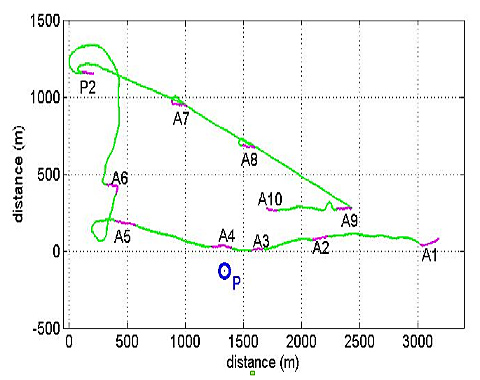
Rayloc-1C
The RAYLOC_1C experiment was aimed at detecting underwater acoustic source at the bottom of shallow seas in real time using a single hydrophone.The boat followed the path shown in the figure below where the boat course is the green line, (P) is the position of the pinger and the stations held in the experiment are shown in purple